 |
Welcome To Evlithium Best Store For Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery |
 |

LiFePO4 cells, also known as lithium iron phosphate batteries, are widely used in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics. Voltage plays a critical role in determining the performance and efficiency of these cells. Understanding the optimal voltage range is crucial for maximizing their potential.
LiFePO4 cells operate within a specific voltage range to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The nominal voltage of a single LiFePO4 cell is approximately 3.2 volts. However, it's important to note that the actual voltage can vary depending on the cell's state of charge and load conditions.
The minimum voltage of a LiFePO4 cell is typically around 2.5 volts. Operating the cell below this threshold can result in irreversible damage and significantly reduce its lifespan. It is crucial to monitor the voltage levels and prevent excessive discharge to maintain the health of the battery.
On the other end of the spectrum, the maximum voltage of a LiFePO4 cell is around 3.6 to 3.8 volts. Going beyond this voltage limit can lead to overcharging, which can cause thermal runaway and compromise the safety of the battery. Therefore, it is essential to employ proper charging mechanisms to prevent overvoltage conditions.
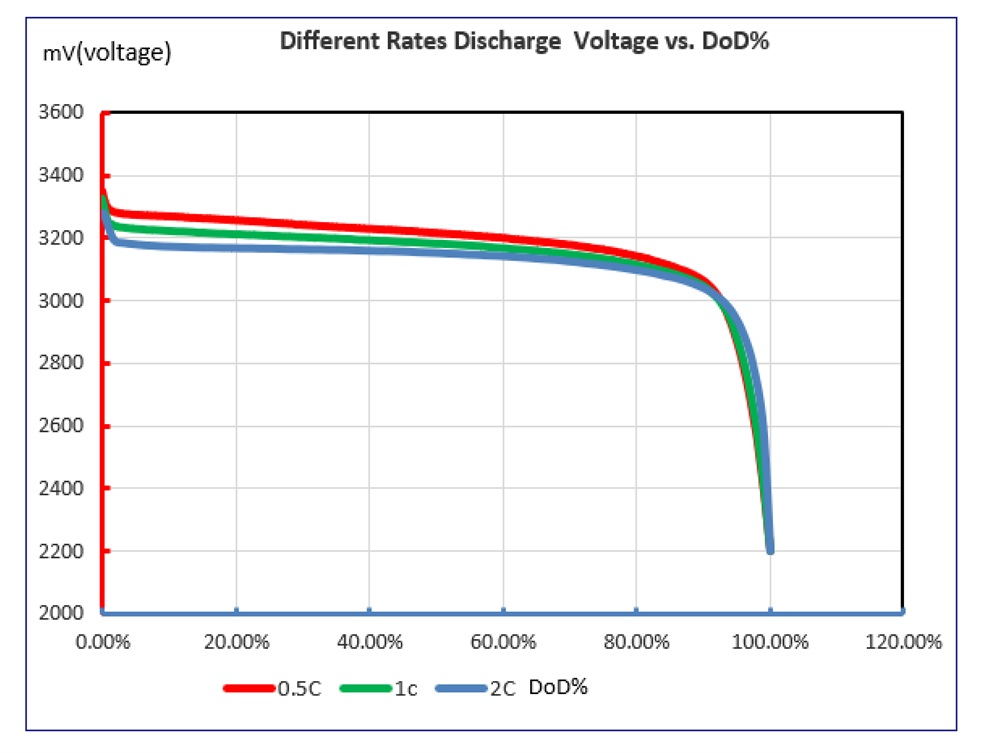
Voltage directly affects the capacity, energy density, and overall performance of LiFePO4 cells. Let's explore how different voltage levels impact the cell's characteristics:
The capacity of a LiFePO4 cell is typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah). Higher voltages enable the cell to store more energy and increase its overall capacity. This means that a LiFePO4 cell with a higher voltage will have a higher energy density, allowing it to power devices for a longer duration.
Voltage also plays a significant role in determining the power output of LiFePO4 cells. A higher voltage can deliver more power, making it suitable for applications that require high-performance capabilities. This is particularly advantageous in electric vehicles and other high-demand scenarios.
Efficiency is a crucial factor in battery-operated systems. LiFePO4 cells operate with high efficiency, and voltage affects this parameter. By maintaining the voltage within the optimal range, you can ensure that the cells operate at their highest efficiency levels, maximizing energy utilization and minimizing wastage.
Edit by editor
All Rights reserved © 2025 Evlithium Limited